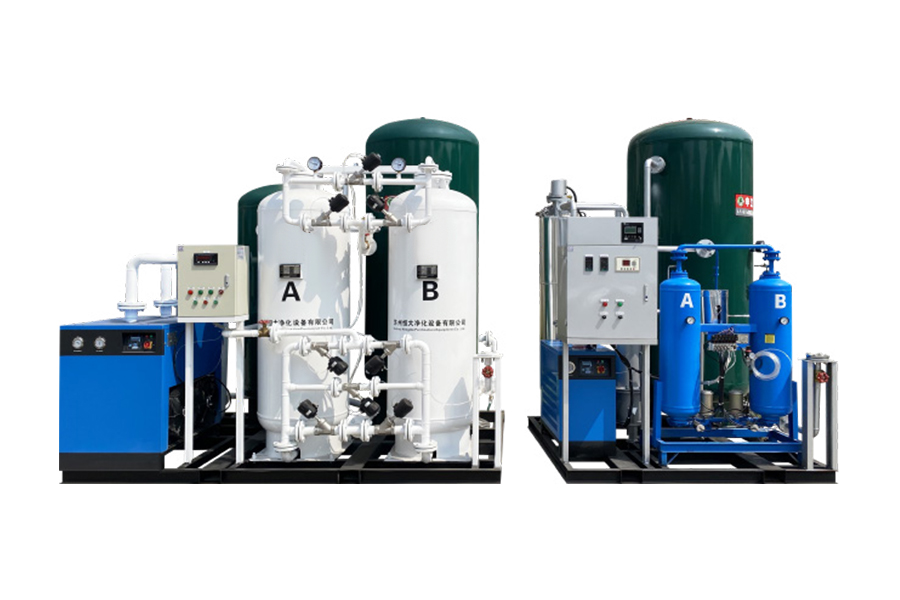
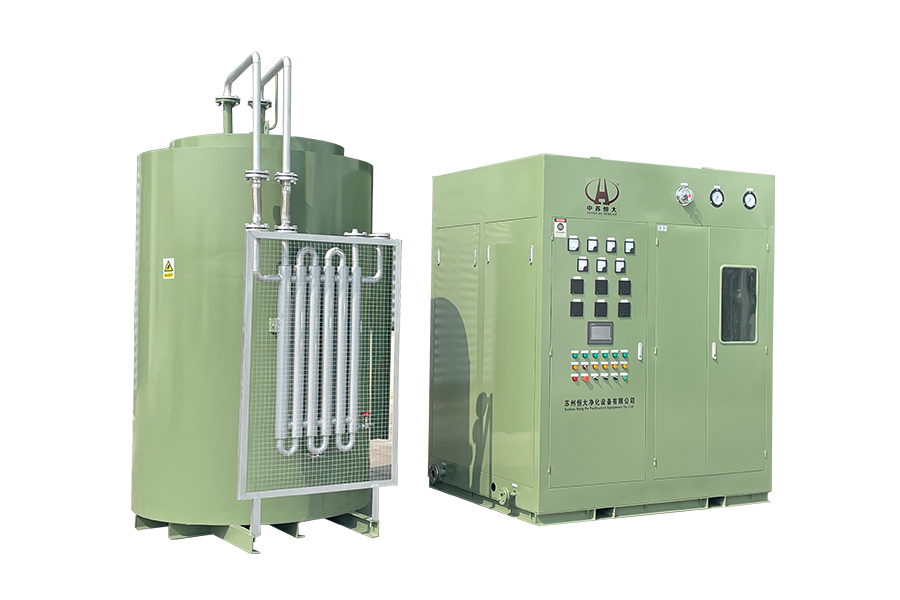
Oxygen is a fundamental element for life. For patients with respiratory conditions or critical illnesses, continuous access to oxygen can mean the difference between stability and severe complications. Hospitals, clinics, and home care settings increasingly rely on medical oxygen generators to provide a steady and reliable oxygen supply.
Understanding Medical Oxygen Generators
Medical oxygen generators are devices designed to produce oxygen from ambient air. Unlike traditional oxygen cylinders, which store compressed oxygen, generators create oxygen on demand. This eliminates dependence on the supply chain for cylinders and reduces the risk of running out of oxygen during critical moments.
The principle behind medical oxygen generators is relatively straightforward. Air contains approximately twenty one percent oxygen, along with nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and other gases. Oxygen generators use a process called pressure swing adsorption to separate oxygen from nitrogen and other gases. This allows the generator to deliver concentrated oxygen to patients in a controlled and safe manner.
There are two main types of medical oxygen generators. Stationary generators are installed in hospitals or healthcare facilities and can supply large volumes of oxygen to multiple patients. Portable generators are smaller and designed for home use, enabling patients to maintain mobility while receiving oxygen therapy.
How Oxygen Generators Work
Medical oxygen generators rely on specialized filters known as zeolite sieves to extract oxygen from the air. The process begins by drawing in ambient air and passing it through a compressor. The compressed air then moves into the zeolite chambers, where nitrogen is absorbed, leaving oxygen behind. This concentrated oxygen is collected in a storage tank or delivered directly to the patient through a flow meter.
Pressure swing adsorption, the technology behind most oxygen generators, involves cycles of pressurization and depressurization. During pressurization, nitrogen is adsorbed by the zeolite. During depressurization, nitrogen is released, regenerating the zeolite for the next cycle. This continuous cycle ensures that oxygen production does not stop and that the generator can provide a constant flow.
In addition to oxygen concentration, modern generators include sensors and alarms to monitor oxygen purity and flow rate. These safety features ensure that patients receive oxygen at therapeutic levels without interruption.
Benefits of Continuous Oxygen Supply
Continuous oxygen supply is crucial for many medical conditions. Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pneumonia, heart failure, or post-surgical complications often require supplemental oxygen to maintain normal blood oxygen levels. Inadequate oxygen supply can lead to hypoxia, organ damage, or even death. Medical oxygen generators reduce these risks by ensuring a stable oxygen source.
For healthcare facilities, generators provide a reliable alternative to oxygen cylinders. Cylinder-based systems require frequent deliveries, which can be affected by logistics, weather, or emergencies. Generators, on the other hand, produce oxygen on site, making them invaluable during peak demand periods or disaster situations.
In home care settings, oxygen generators allow patients to live independently while receiving necessary therapy. Portable models offer flexibility, enabling patients to move freely without worrying about cylinder replacement or running out of oxygen.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
To ensure continuous operation, medical oxygen generators require regular maintenance. Filters and compressors should be checked periodically to prevent blockages and ensure optimal performance. Zeolite sieves may require replacement over time, depending on usage and manufacturer guidelines.
Safety is another important consideration. Although oxygen is essential for life, it is also highly reactive. Generators must be placed in well-ventilated areas, away from open flames or flammable materials. Many generators include built-in alarms to alert caregivers if oxygen purity drops or if a component fails.
Training for healthcare professionals and caregivers is also essential. Proper operation, maintenance, and emergency protocols help minimize the risk of equipment failure and ensure that patients continue to receive uninterrupted oxygen.
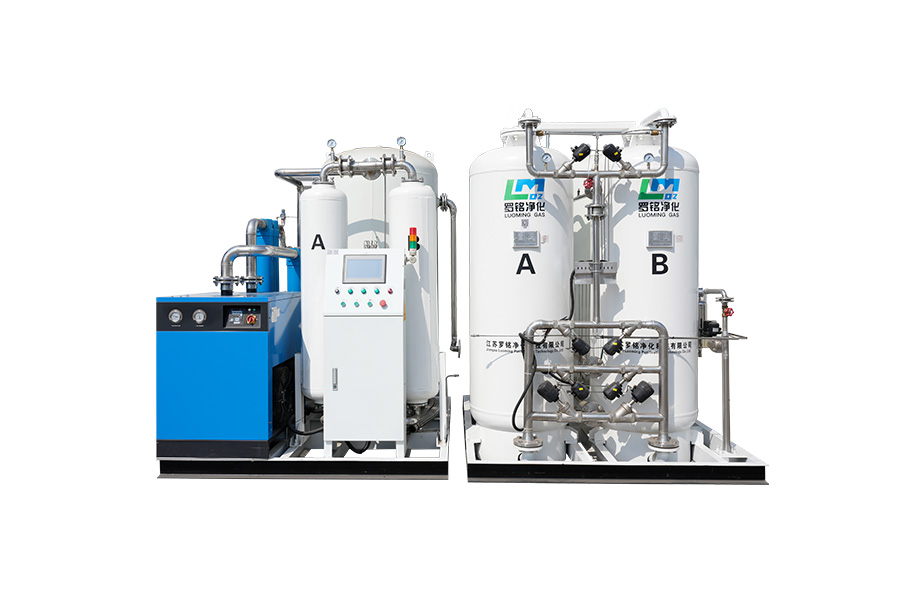

Applications in Hospitals and Clinics
In hospitals, medical oxygen generators are often integrated into central supply systems. These systems distribute oxygen through pipelines to patient rooms, operating theaters, and intensive care units. The advantage of this approach is that a single generator can serve multiple patients simultaneously, reducing the need for numerous cylinders.
Generators are especially valuable in emergency rooms and intensive care units, where oxygen demand can fluctuate rapidly. They provide a reliable supply during peak usage periods and reduce the risk of shortages during critical situations.
Medical oxygen generators are also useful in outpatient clinics and rural healthcare facilities. In locations where cylinder delivery is difficult, generators provide a practical solution for ensuring continuous oxygen availability. This is particularly important in regions with limited healthcare infrastructure or during public health emergencies.
Advantages Over Traditional Oxygen Cylinders
While oxygen cylinders have been the standard for decades, generators offer several advantages. First, they eliminate the need for frequent refills and logistics management. This reduces operational costs and the potential for supply disruptions. Second, generators provide a consistent flow of oxygen, whereas cylinder pressure can decrease over time, affecting delivery. Third, on-site oxygen production is more environmentally friendly, as it reduces the carbon footprint associated with transporting cylinders.
Additionally, oxygen generators allow for better control of oxygen concentration and flow rate. Healthcare providers can adjust settings according to patient needs, ensuring precise therapy. Modern generators can deliver oxygen concentrations of ninety five percent or higher, comparable to that of medical-grade cylinders.
Portable Oxygen Generators for Home Care
Portable oxygen generators have become increasingly popular in home care settings. These devices are compact, lightweight, and designed for mobility. They allow patients with chronic respiratory conditions to maintain an active lifestyle without interruption to therapy.
Portable generators typically include rechargeable batteries, allowing use during travel or power outages. Some models are designed to operate quietly, making them suitable for day-to-day home use. Despite their small size, these devices deliver a reliable flow of oxygen, ensuring that patients receive continuous therapy even outside a hospital setting.
Role During Public Health Emergencies
Medical oxygen generators have played a critical role during public health emergencies, including respiratory disease outbreaks. In situations where oxygen demand exceeds cylinder supply, generators provide a scalable solution to maintain patient care. Hospitals can increase oxygen production without waiting for external deliveries, ensuring that all patients receive necessary treatment.
During natural disasters or logistical disruptions, oxygen generators provide a lifeline for healthcare facilities and home care patients alike. Their ability to produce oxygen on site ensures continuity of care, even in challenging circumstances.
Future Developments
The technology behind medical oxygen generators continues to evolve. Research is focused on improving efficiency, portability, and oxygen purity. Advances in materials and filtration systems are expected to extend the lifespan of generators and reduce maintenance requirements. Smart sensors and digital monitoring systems are also being integrated, enabling real-time tracking of oxygen flow and purity for enhanced safety.
In the future, oxygen generators may become standard equipment in more healthcare settings, including smaller clinics and emergency response units. Their ability to provide continuous oxygen supply reliably and efficiently makes them indispensable in modern healthcare.
Conclusion
Medical oxygen generators are vital for ensuring continuous oxygen supply in hospitals, clinics, and home care settings. By producing oxygen on demand and delivering it reliably, they reduce dependence on cylinders and help maintain patient safety. From intensive care units to home therapy, these devices provide a consistent flow of oxygen, supporting recovery, treatment, and quality of life. With proper maintenance and safety practices, medical oxygen generators will continue to play a critical role in respiratory care and emergency preparedness for years to come.



 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español عربى
عربى


