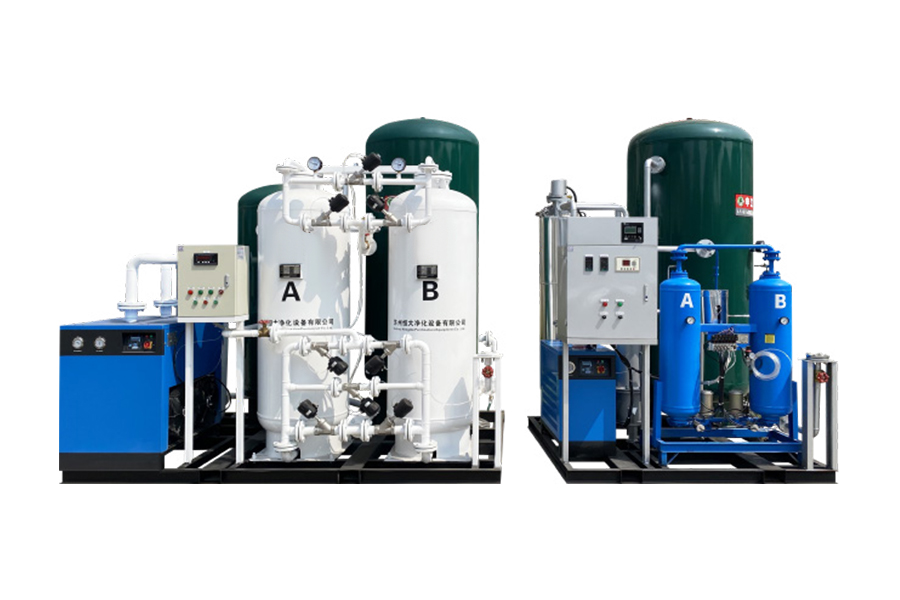
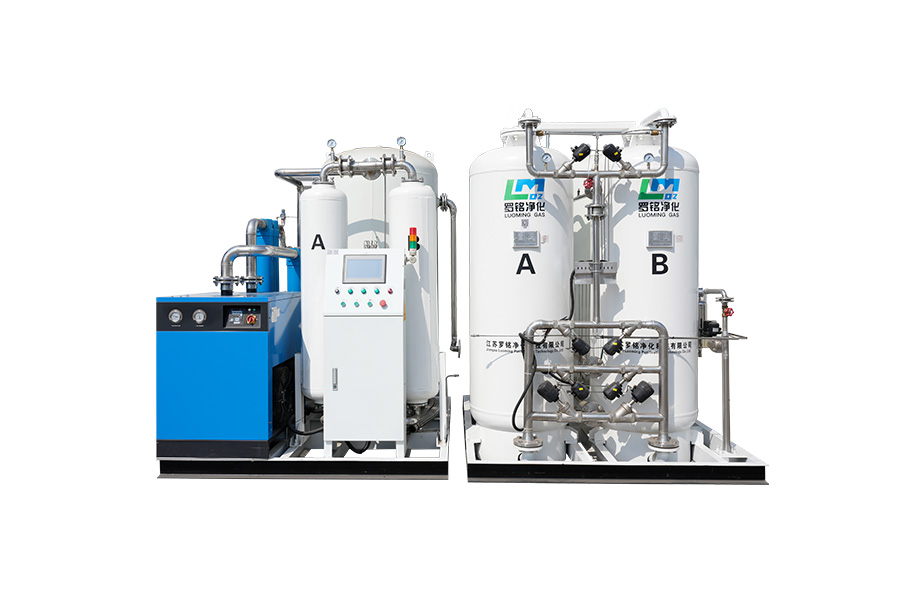
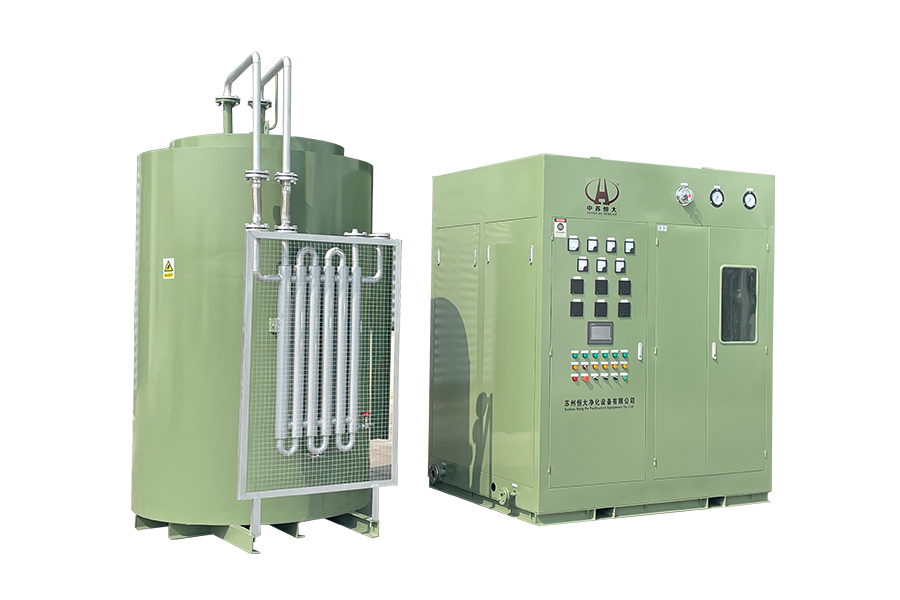
A Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) nitrogen generator produces high‑purity nitrogen gas from compressed air without liquid nitrogen deliveries. PSA nitrogen generator systems are widely used in food packaging, electronics manufacturing, laser cutting, and chemical processing. They work by using adsorbent materials—typically carbon molecular sieves (CMS)—to separate oxygen and other gases from nitrogen. The result is a consistent flow of nitrogen at specified purities (typically 95%–99.999%), which can reduce operating costs, improve quality, and enhance safety compared to traditional supply methods.
Core Components of a PSA Nitrogen Generator
Understanding the key components of a PSA nitrogen generator helps you select and operate the right system for your needs. Each element contributes to performance, efficiency, and maintenance requirements.
Air Compressor and Pre‑Filtration
The PSA process begins with an air compressor capable of delivering clean, dry compressed air at the required pressure. Pre‑filtration stages remove particulates, oil, and moisture to protect downstream components. Typical pre‑filtration includes coalescing filters and activated carbon filters. Moisture and contaminants reduce adsorbent life and compromise nitrogen purity.
Adsorption Towers with Carbon Molecular Sieves (CMS)
The heart of the PSA nitrogen generator is the pair of adsorption towers filled with CMS. During operation, one tower adsorbs oxygen and other trace gases while the other regenerates by venting the adsorbed gases. This alternating process allows continuous nitrogen production. The size and quality of CMS determine achievable purity and cycle time.
Control Valves and Automation
Precise control valves and automated sequencing ensure adsorption and regeneration occur at the right time. Programmable logic controllers (PLC) or dedicated gas generator controllers manage the switching of towers, monitor pressures, and adjust cycles to maintain target nitrogen purity. Modern systems also include interfaces for remote monitoring and alarm reporting.
Step‑by‑Step Guide to Selecting a PSA Nitrogen Generator
Selecting the appropriate PSA nitrogen generator requires a practical assessment of your facility’s gas requirements, quality needs, and operating constraints. Follow these steps to match system specifications with your application.
Determine Your Nitrogen Flow Rate Requirements
Calculate your peak and average nitrogen consumption in standard cubic feet per minute (SCFM) or normal cubic meters per hour (Nm³/hr). Consider future production expansion. Choosing a generator with at least a 10% higher capacity than your current requirement helps avoid shortages during peak usage.
Define Target Nitrogen Purity
Different applications require different nitrogen purity levels. For example:
- Food packaging: 95%–99% nitrogen to prevent oxidation and spoilage.
- Laser cutting: 99.9%+ to reduce oxidation at high temperatures.
- Electronics manufacturing: >99.999% for sensitive processes.
Defining your purity target impacts system size, cycle design, and adsorbent choice.
Evaluate Available Space and Installation Constraints
PSA nitrogen generators range from compact skids to large modular systems. Assess floor space, ceiling height, and proximity to utilities like power and compressed air. Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent heat buildup and allow space for maintenance access.
Installation Best Practices for PSA Nitrogen Systems
Proper installation ensures reliable, efficient performance. Below are essential considerations during setup and commissioning.
Pre‑Installation Checklist
Before installation, verify:
- Compressed air quality meets required ISO standards (typically ISO 8573‑1 Class 1.4.1 or better).
- Electrical supply matches system requirements and includes proper grounding.
- Vibration and noise isolation measures are planned if the generator is near sensitive equipment.
These steps prevent early failures and ensure warranty compliance.
Mounting and Airflow Considerations
Install the generator on a level surface to prevent skewed valve operation. Allow at least 2 feet of clearance on all sides for service access. Maintain unobstructed airflow around the unit, as heat generated during adsorption and regeneration cycles must dissipate effectively.
Operating a PSA Nitrogen Generator Efficiently
Once installed, operate your PSA nitrogen generator efficiently to maximize uptime and minimize costs. The following points address common operational practices.
Start‑Up and Stabilization
During initial start‑up, the generator may take several hours to reach stable nitrogen purity. Do not connect critical processes until purity stabilization is confirmed by onboard analyzers or external meters. Gradual loading prevents premature wear on valves and adsorbents.
Monitoring Purity and Pressure
Continuously monitor nitrogen purity with calibrated sensors. Typical control systems display purity, flow, and pressure in real time. Set alarms for deviations beyond agreed limits. Frequent pressure swings outside design parameters often indicate filter clogging, air leaks, or CMS exhaustion.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance extends service life and preserves performance:
| Maintenance Task |
Frequency |
Purpose |
| Pre‑filter replacement |
Every 3–6 months |
Prevents compressor oil and particulates from reaching CMS |
| Carbon molecular sieve (CMS) inspection |
Annually |
Checks for degradation and loss of adsorption capacity |
| Valve and sensor calibration |
Every 6 months |
Ensures timing accuracy and purity readings |
Common Troubleshooting Scenarios and Fixes
Even well‑maintained systems can experience issues. Here are practical solutions to common problems.
Low Nitrogen Purity
If nitrogen purity falls below targets:
- Check for wet or oily compressed air; improve filtration or dryer performance.
- Inspect CMS beds for saturation or damage; consider replacement.
- Verify valve timing; malfunctioning valves often reduce effective adsorption time.
Pressure Fluctuations
Pressure irregularities frequently stem from air leaks or improper compressor output. Use calibrated gauges to isolate leaks in piping or fittings. Ensure the compressor delivers stable pressure within the generator’s design range.
Safety Considerations When Working with PSA Nitrogen Generators
Nitrogen is an inert gas that displaces oxygen. While not toxic, it can cause asphyxiation in confined spaces. Key safety practices include:
- Label outlets and storage lines clearly to prevent accidental oxygen displacement.
- Install oxygen sensors in enclosed areas where nitrogen could accumulate.
- Train personnel on nitrogen hazards and emergency procedures.
Implementing these safeguards reduces risk and supports compliance with workplace standards.



 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español عربى
عربى


