Understanding Medical Oxygen Generators and Their Clinical Purpose
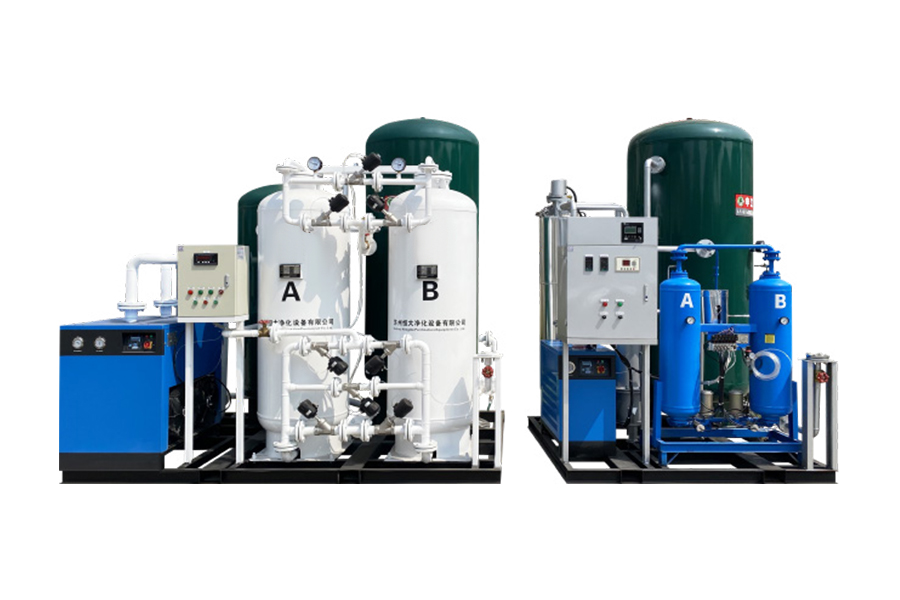
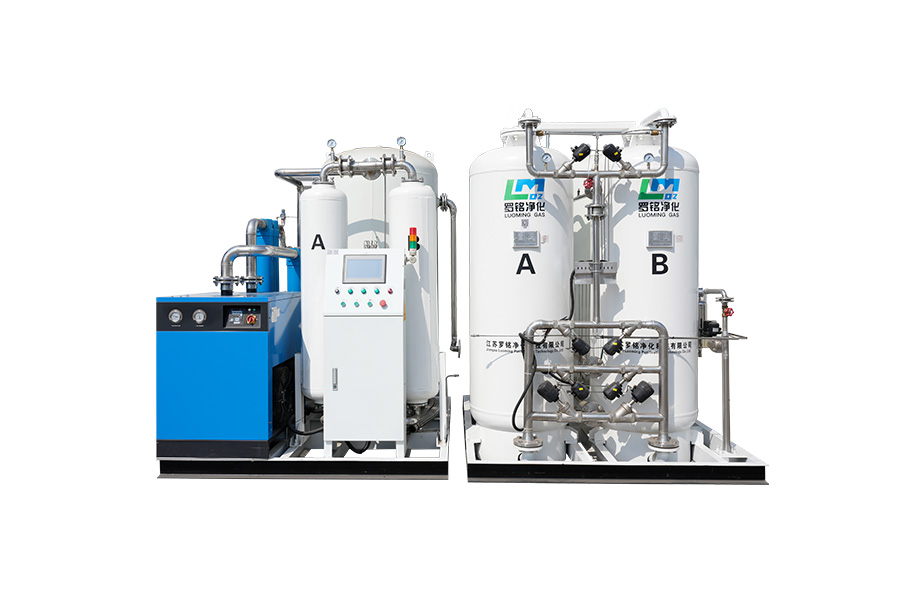
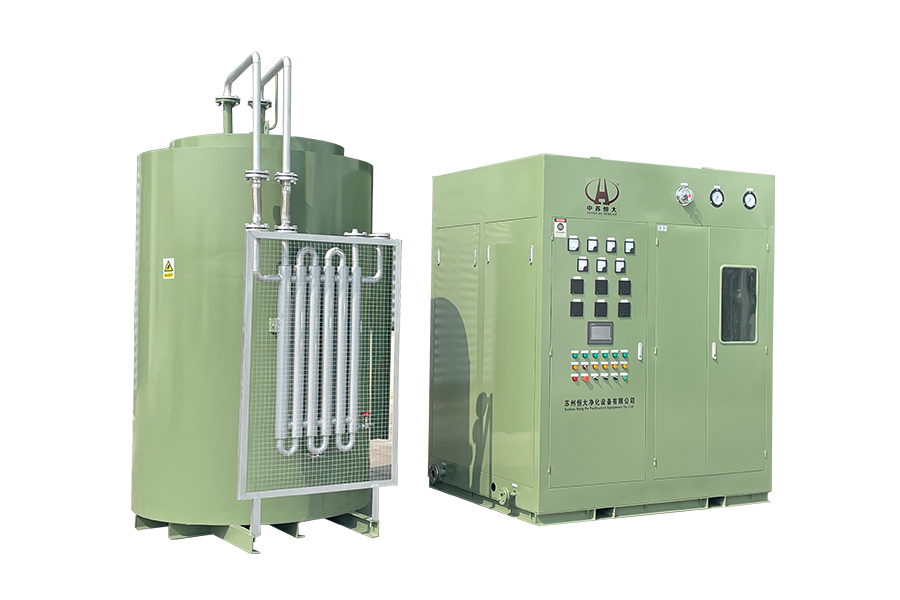
Medical oxygen generators are specialized devices designed to produce medical-grade oxygen on-site by separating oxygen from ambient air. Unlike oxygen cylinders or liquid oxygen systems, these generators supply a continuous flow of oxygen without relying on frequent refills. They are widely used in hospitals, clinics, emergency centers, nursing homes, and home healthcare settings where stable oxygen availability is critical.
The primary purpose of medical oxygen generators is to ensure uninterrupted oxygen therapy for patients with respiratory conditions such as COPD, pneumonia, asthma, post-surgical hypoxia, and chronic lung disease. Their ability to deliver oxygen at consistent purity levels makes them essential medical equipment in both acute and long-term care environments.
How Medical Oxygen Generators Work in Real Applications
Most medical oxygen generators operate using Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) technology. This process filters nitrogen from compressed air using molecular sieve materials, allowing concentrated oxygen to pass through. The result is medical oxygen with purity levels typically ranging from 90% to 96%, which meets international healthcare standards for oxygen therapy.
In real-world clinical applications, these generators are connected directly to oxygen pipelines, ventilators, anesthesia machines, or oxygen flowmeters. Their automated operation minimizes human intervention, while built-in monitoring systems ensure pressure stability, oxygen purity, and alarm signaling during abnormal conditions.
Key Performance Parameters When Evaluating Medical Oxygen Generators
Selecting the right medical oxygen generator requires careful evaluation of performance indicators that directly affect patient safety and operational efficiency. These parameters determine whether the system can meet clinical demand without compromising oxygen quality.
- Oxygen purity stability under continuous operation
- Flow rate capacity measured in liters per minute
- Outlet pressure compatibility with hospital pipelines
- Noise level for patient-friendly environments
- Power consumption and backup power support
Medical-grade oxygen generators should also comply with ISO, CE, or FDA standards to ensure safe use in regulated healthcare environments.
Comparison of Medical Oxygen Generators and Traditional Oxygen Supply Systems
Healthcare facilities often compare oxygen generators with cylinders and liquid oxygen tanks when planning oxygen infrastructure. Each solution has advantages, but oxygen generators offer distinct long-term benefits.
| Supply Method |
Refill Dependency |
Operational Cost |
Supply Stability |
| Medical Oxygen Generator |
None |
Low |
Continuous |
| Oxygen Cylinders |
High |
High |
Intermittent |
| Liquid Oxygen Tanks |
Medium |
Medium |
Stable |
Clinical Settings That Benefit Most from Medical Oxygen Generators
Medical oxygen generators are especially valuable in facilities where uninterrupted oxygen is essential. Their adaptability makes them suitable for both centralized and decentralized oxygen supply systems.
- Hospitals with intensive care and surgical departments
- Emergency and trauma centers
- Rural clinics with limited oxygen delivery access
- Home healthcare environments requiring long-term oxygen therapy
In developing regions or remote areas, on-site oxygen generation significantly reduces supply chain risks and improves patient outcomes during emergencies.
Installation and Infrastructure Considerations
Proper installation is crucial to maximize the efficiency and lifespan of medical oxygen generators. Facilities must ensure adequate ventilation, stable electrical supply, and appropriate space for maintenance access.
Integration with existing oxygen pipelines requires pressure regulation systems, backup oxygen sources, and compliance with medical gas installation standards. Many healthcare providers also include secondary oxygen cylinders as emergency backups.
Maintenance Practices That Ensure Long-Term Reliability
Routine maintenance directly affects oxygen purity and equipment reliability. Medical oxygen generators are designed for continuous operation, but preventive care is essential.
- Regular replacement of air intake filters
- Monitoring molecular sieve performance
- Calibration of oxygen purity sensors
- Inspection of compressors and valves
Scheduled servicing reduces downtime and ensures consistent compliance with medical oxygen standards.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Medical oxygen generators must meet strict regulatory requirements to be used in healthcare environments. Compliance with ISO 13485, ISO 7396, CE certification, or FDA regulations confirms that the system meets medical safety and performance benchmarks.
Safety features such as oxygen purity alarms, pressure alerts, and automatic shutdown mechanisms protect both patients and medical staff from potential risks.
Cost Efficiency and Long-Term Operational Value
While the initial investment in medical oxygen generators may be higher than cylinder-based systems, long-term operational savings are substantial. Facilities reduce recurring expenses related to oxygen refilling, transportation, and storage.
Over time, on-site oxygen generation delivers predictable costs, improved supply security, and greater control over oxygen availability, making it a sustainable solution for modern healthcare systems.



 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español عربى
عربى


